| Oracle® TimesTen In-Memory Database Operations Guide Release 11.2.1 Part Number E13065-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® TimesTen In-Memory Database Operations Guide Release 11.2.1 Part Number E13065-03 |
|
|
View PDF |
To access TimesTen data stores on remote machines, applications use the TimesTen Client driver to communicate with the TimesTen Server process. Using the TimesTen Client, applications written to use the TimesTen Data Manager can connect transparently to TimesTen data stores on any remote or local machine that has the TimesTen Server Daemon and Data Manager installed.
The TimesTen Server is a process that runs on a server machine. You can install the TimesTen Client on a separate or the same machine as the TimesTen Server. If you install the TimesTen Client on the same machine as the TimesTen Server, you can use them to access TimesTen data stores on the local machine. For example, this is useful when you want a 32-bit application to access a 64-bit data store on the same machine, for platforms that support both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
Note:
You can create a client/server connection between any combination of platforms that TimesTen supports.You can link a client either directly with the TimesTen Client driver or with a driver manager. The latter is typical for Windows, which includes a driver manager, but not for UNIX. TimesTen supplies a driver manager for either Windows or UNIX with the Quick Start sample applications. Note that there are performance considerations in using a driver manager.
Note:
For details on compiling TimesTen applications, see the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Java Developer's Guide or the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database C Developer's Guide.The main topics in this chapter are:
The following are the restrictions on client/server communication:
XLA cannot be used over a client/server connection.
On UNIX, some TimesTen utilities only work over direct connections, such as ttAdmin, ttRepAdmin, and ttBackup. The utilities that can be executed over a client connection on the UNIX platform are named with a suffix of CS, such as ttIsqlCS, ttBulkCpCS, ttMigrateCS and ttSchemaCS. These utilities have been linked with the ODBC driver manager, so they can be used with both client/server and direct linked drivers. Each utility listed in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference provides the name of the client/server version of that utility, if there is one.
The ttCacheUidPwdSet built-in cannot be used over a client connection.
You cannot connect with an external user defined on one host to a TimesTen data source on a remote host. There are no restrictions for connecting with internal users.
Internal users can only be created or altered over a direct connection and not over a client connection to a TimesTen database. Thus, you can only execute the CREATE USER or ALTER USER statements using a direct connection to the TimesTen database. Once created, the user that connects from the client to the server must be granted the CREATE SESSION privilege or the connection will fail. For more information on how to create the user on the TimesTen database and how the administrator grants the CREATE SESSION privilege, see "Creating or identifying users to the database" and "Granting privilege to connect to the database".
By default, a Server process is spawned at the time a client requests a connection. By setting the -serverPool option in the ttendaemon.options file on the Server machine, you can pre-spawn a reserve pool of Server processes. See "Prespawning TimesTen Server processes" for details.
When using TimesTen Client/Server there are three ways the TimesTen Client can communicate with the TimesTen Server.
By default, the TimesTen Client communicates with the TimesTen Server daemon using TCP/IP sockets. This is the only form of communication available when the TimesTen Client and Server are installed on different machines.
If both the TimesTen Client and Server are installed on the same machine, applications using the TimesTen Client ODBC driver may improve performance by using a shared memory segment for inter-process communication (IPC). Using a shared memory segment allows for the best performance, but consumes more memory. To use a shared memory segment as communication, you must set the server options in the ttendaemon.options file. See "Using shared memory for Client/Server IPC". You must also define the Network Address of the logical server as ttShmHost. See "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on Windows" or "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on UNIX".
Note:
TimesTen supports a maximum of 16 different instances of the shared memory IPC-enabled server. If an application tries to connect to more than 16 different shared memory segments it receives an error.On UNIX platforms, if both the TimesTen Client and Server are installed on the same machine, you can use UNIX domain sockets for communication. Using a shared memory segment allows for the best performance, but greater memory usage. Using UNIX domain sockets allows for improved performance over TCP/IP, but with less memory consumption than a shared memory segment connection. To use domain sockets, you must define the Network Address of the logical server as ttLocalHost. See "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on Windows" or "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on UNIX" for more information.
Note:
Before configuring the TimesTen Client and Server, read "TimesTen ODBC and JDBC drivers" and "Data source names".The following sections describe how to connect a TimesTen application to a TimesTen data store using TimesTen Client and Server:
Perform the following to configure TimesTen when the client and server are of the same TimesTen release:
Install the TimesTen Server on the machine on which the TimesTen data store resides. This machine is called the "server machine." For information on how to install the TimesTen Server, see the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Installation Guide.
Install the TimesTen Client on the machine where the client application resides. This machine is called the "client machine." For information on how to install the TimesTen Client, see the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Installation Guide.
If you are using JDBC to connect to the database, install the Java Developer's Kit (JDK) on the client machine, where the Java application will be running and set up the environment variables, such as CLASSPATH and LIBRARY PATH, on the client machine. See "Setting the Java environment variables" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Java Developer's Guide for details.
On the server machine, create and configure a Server DSN corresponding to the TimesTen data store. See "Defining Server DSNs".
On the client machine, create and configure a Client DSN corresponding to the Server DSN. See "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on UNIX" and "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on Windows".
For OCI and Pro*C client/server connections, configure the application to use either tnsnames.ora or easy connect on the client as described in "Connecting to a TimesTen Datastore from OCI" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database C Developer's Guide.
Set TimesTen Client connection attributes. See "Data Store Attributes" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
Link client/server applications as follows:
Link C and C++ client/server applications as described in "Linking options" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database C Developer's Guide.
Link OCI or Pro*C applications in the same manner as any OCI or Pro*C direct mode applications are linked, which is described in "TimesTen Support for Oracle Call Interface" and "TimesTen Support for the Oracle Pro*C/C++ Precompiler" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database C Developer's Guide.
A TimesTen Client can connect to a TimesTen Server from a different release and of a different bit level.
A TimesTen Client 6.0 release may connect to a TimesTen Server 6.0 or 7.0 release of any bit level.
Note:
For a TimesTen 6.0 Client to connect successfully to a TimesTen Server release 7.0, the-insecure-backwards-compat option must be set in the ttendaemon.options file for the TimesTen Server.A TimesTen Client 7.0 or later release may connect to a TimesTen Server 7.0 or later release of any bit level.
The TimesTen Server loads a driver and a TimesTen database of its own release and bit level when the TimesTen Client connects to the Server. The TimesTen Data Manager must be installed on the Server host.
If you are using a local client/server connection using UNIX Domain sockets through ttLocalHost, then the platforms for the client and the server must be UNIX. The bit level and the release level for the client and server hosts must be the same.
If you are using a local client/server connection over a shared memory IPC using ttShmHost, then the platforms for the client and server can be either Windows or UNIX. The bit level may be different on the client and server hosts.
The TimesTen Server daemon is a subdaemon of the TimesTen daemon. If you have the TimesTen Server installed with no client installation, the TimesTern Server is automatically started and stopped when the TimesTen daemon or Service is started or stopped. You can explicitly start or shut down the daemon or Service with the ttDaemonAdmin utility.
The TimesTen Server daemon handles requests from applications linked with the TimesTen Client driver.
The default ports for the 32-bit and 64-bit versions of TimesTen main and Server daemons are described in the "TimesTen Install" chapter in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Installation Guide. System administrators can change the port number during installation to avoid conflicts or for security reasons. The port range is from 1 - 65535. To connect to the TimesTen Server, Client DSNs are required to specify the port number as part of the logical server name definition or in the connection string.
On Windows, the TimesTen Service is run as user SYSTEM. On UNIX, the TimesTen Server is run as the instance administrator.
For instructions on modifying TimesTen Server daemon options, see "Modifying the TimesTen Server daemon options".
By default, TimesTen creates only one connection to a Server per child process.
Because a TimesTen Server DSN corresponds to data stores that are accessed by a TimesTen Server daemon, a TimesTen Server DSN can be configured using regular connection attributes. In addition, you can specify connection attributes that allow you to specify multiple client connections to a single Server.
You can configure these attributes as part of the Server DSN definition or you can configure these attributes in the TimesTen daemon options file (ttendaemon.options). For a description of the TimesTen daemon options see "Specifying multiple connections to the TimesTen Server".
The Server Connection attributes are MaxConnsPerServer, ServersPerDSN, and ServerStackSize. For a complete description of the TimesTen Server connection attributes, see "Data Store Attributes" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
Server DSNs correspond to data stores that are accessed by a TimesTen Server Daemon. You can add or configure a Server DSN while the TimesTen Server is running.
A Server DSN is a TimesTen data manager system DSN. For a description of DSNs and instructions on creating them, see "Creating a DSN on Windows" or "Creating a DSN on UNIX". If you anticipate having more than one connection to the Server DSN, specify appropriate values for the Server attributes as needed. On Windows, these are specified on the Server tab.
You can configure connection attributes used by the TimesTen Client driver as part of the Client DSN definition. Alternatively, you can configure connection attributes at runtime in the connection string that is passed to the ODBC SQLDriverConnect function or the URL string that is passed to the JDBC DriverManager.getConnection() method.
The DataStore connection attribute is not allowed in the TimesTen Client connection string.
Use the TTC_SERVER_DSN attribute in either the connection string or the Client DSN for a client to specify which DSN it should use on the server. The server optionally uses the DRIVER attribute in the DSN to specify what driver to load.
Note:
The TimesTen Client allows TimesTen Data Manager attributes to be passed in as part of the connection or URL string. However, the client ignores any Data Manager attributes specified in the ODBC.INI file as part of the TimesTen Client DSN definition.For a complete description of the TimesTen Client connection attributes, see "Data Store Attributes" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
On Windows, use the ODBC Data Source Administrator to configure logical server names and to define Client DSNs.
This section includes the following topics:
To create and configure a logical server name:
On the Windows Desktop, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC).
This opens the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Click User DSN or System DSN.
Select a TimesTen Client DSN and click Configure. If no Client DSN exists, click Add, select TimesTen Client 11.2.1 and click Finish. This opens the TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog.
Click Servers. This opens the TimesTen Logical Server List dialog.
Click Add. This opens the TimesTen Logical Server Name Setup dialog.
In the Server Name field, enter a logical server name.
In the Description field, enter an optional description for the server.
In the Network Address field, enter the host name or IP address of the server machine. The Network Address must be one of:
| Type of connection | Network Address |
|---|---|
| Local client/server connection that uses shared memory for inter-process communication | ttShmHost |
| Remote client/server connection | The name of the machine where the TimesTen Server is running. For example, server. mycompany.com |
In the Network Port field, TimesTen displays the port number on which the TimesTen Logical Server Listens by default. If the TimesTen Server is listening on a different port, enter that port number in the Network Port field.
For example:
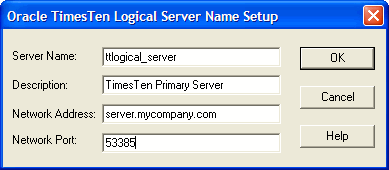
Click OK, then click Close in the TimesTen Logical Server List dialog to finish creating the logical server name.
To define a TimesTen Client DSN:
On the Windows Desktop, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC). This opens the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Choose either User DSN or System DSN. For a description of User DSNs and System DSNs see "Data source names".
Click Add. This opens the Create New Data Source dialog.
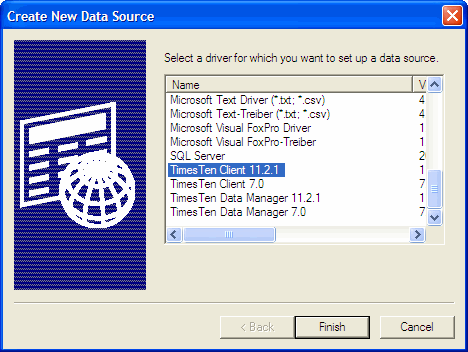
Choose TimesTen Client 11.2.1. Click Finish. This opens the Oracle TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog.
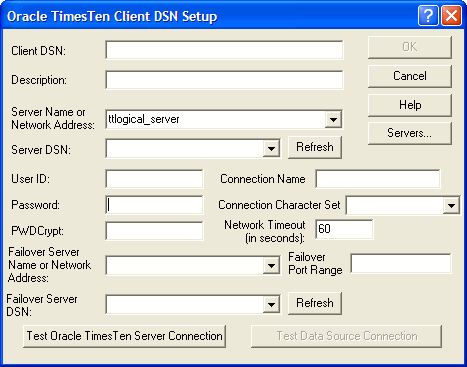
In the Client DSN field, enter a name for the Client DSN.
The name must be unique to the current list of defined DSNs on the machine where the client application resides and can contain up to 32 characters. To avoid potential conflicts, you may want to use a consistent naming scheme that combines the logical server name with the name of the Server DSN. For example, a corporation might have Client DSNs named Boston_Accounts and Chicago_Accounts where Boston and Chicago are logical server names and Accounts is a Server DSN.
In the Description field, enter an optional description for the Client DSN.
In the Server Name or Network Address field, specify the logical server or network address of the server machine.
The name can be a host name, IP address or logical server name. The logical server names defined on the client machine can be found in the drop-down list. To define logical server names, click Servers.
If you do not specify a logical server name in this field, the TimesTen Client assumes that the TimesTen Server Daemon is running on the default TCP/IP port number. Therefore, if your Server is running on a port other than the default port and you do not specify a logical server name in this field, you must specify the port number in the ODBC connection string, using the TCP_Port attribute.
For more information on defining logical server names, see "Creating and configuring a logical server name".
In the Server DSN field, enter the Server DSN corresponding to the data store that the client application will access.
If you do not know the name of the Server DSN, click Refresh to obtain a list of Server DSNs that are defined on the machine specified in the Server Name or Network Address field. Select the Server DSN from the drop-down list.
You must have a network connection to the machine where the TimesTen Server is running.
In the Connection Character Set field, choose a character set that matches your terminal settings or your data source. The default connection character set is US7ASCII. For more information, see "ConnectionCharacterSet" in Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
You can configure automatic client failover for data stores that have active standby pair replication schemes. This enables the client to fail over automatically to the server on which the standby data store resides.
See "Automatic client failover" in Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database C Developer's Guide for information about connection option persistence after failover.
In the Oracle TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog, complete the following fields:
In the Failover Server Name or Network Address field, specify the logical server or network address of the server machine.
The name can be a host name, IP address or logical server. The logical server names defined on the client machine can be found in the drop-down list. To define logical server names, click Servers.
If you do not specify a logical server name in this field, the TimesTen Client assumes that the TimesTen Server Daemon is running on the default TCP/IP port number. Therefore, if the Server is running on a port other than the default port and you do not specify a logical server name in this field, you must specify the port number in the ODBC connection string, using the TCP_Port attribute.
For more information on defining logical server names, see "Creating and configuring a logical server name".
In the Failover Server DSN field, enter the Server DSN corresponding to the standby data store.
If you do not know the name of the Server DSN, click Refresh to obtain a list of Server DSNs that are defined on the machine specified in the Failover Server Name or Network Address field. Select the Server DSN from the drop-down list.
You must have a network connection to the machine where the TimesTen Server is running.
Optionally, specify the Failover Port Range for the port for failover notifications. By default, TimesTen uses a port chosen by the operating system. To accommodate firewalls between the client and server systems, you can specify one value for the port number or a range of port numbers.
For a description of the Timeout, UID and PWD attributes, see "Data Store Attributes" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
To set the timeout interval and authentication:
In the User ID field of the Oracle TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog box, enter a user name that is defined on the server machine.
In the Password field, enter the password that corresponds to the user ID. Alternatively, you can enter an encrypted password in the PwdCrypt field.
In the Timeout Interval field, enter the interval time in seconds. You can enter any non-negative integer. A value of 0 indicates that client/server operations should not time out. The default is 60 seconds. The maximum is 99,999 seconds.
Click OK to save the setup.
To delete a server name:
On the Windows Desktop on the client machine, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel.
Double click ODBC. This opens the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Select a TimesTen Client DSN and click Configure. This opens the TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog.
Click Servers. This opens the TimesTen Logical Server List dialog.
Select a server name from the TimesTen Servers list.
Click Delete.
In this example, the TimesTen Client machine is client.mycompany.com. The client application is accessing the Server DSN on the remote server machine, server.mycompany.com. The logical name of the server is ttserver_logical.
Note:
These examples reference the 32-bit sample DSNs. This is indicated by the extension_32. On 64-bit platforms, the sample DSNs are appended with _64.On the server machine server.mycompany.com, use the ttStatus utility to verify that the TimesTen Server Daemon is running and to verify the port number it is listening on.
Using the procedure in "Defining Server DSNs", verify that the Server DSN, RunData1121_32, is defined as a System DSN on server.mycompany.com.
On the client machine, client.mycompany.com, create a logical Server Name entry for the remote TimesTen Server. In the TimesTen Logical Server Name Setup dialog:
In the Server Name field, enter ttserver_logical.
In the Network Address field, enter server.mycompany.com.
In the Network Port field, enter 53385. This is the default port number for the TimesTen Server on 32-bit platforms for TimesTen Release 11.2.1. This value should correspond to the value displayed by ttStatus in Step 1.
See "Creating and configuring a logical server name" for the procedure to open the TimesTen Server Name dialog and for more details.
On the client machine, client.mycompany.com, create a Client DSN that corresponds to the remote Server DSN, RunData_tt1121_32. In the TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog, enter the following values:
In the Client DSN field, enter RunDataCS_tt1121_32.
In the Server Name or Network Address field, enter ttserver_logical.
In the Description field, enter a description for the server. Entering data into this field is optional.
In the Server DSN field, enter RunData1121_32.
Run the client application from the machine client.mycompany.com using the Client DSN, RunDataCS_tt1121. The example below uses the ttIsqlCS program installed with TimesTen Client.
ttIsqlCS connStr "DSN=RunDataCS_tt1121_32"
This example describes how to access a TimesTen Server that is listening on a port numbered other than the default port number.
Consider that the Network Address of the TimesTen Server is server.mycompany.com and the Server is listening on Port 53385. The following methods can be used to connect to a Server DS:
Define the logical server name logical_server with server.mycompany.com as the Network Address and 53385 as the Network Port. Define a Client DSN with logical_server as the Server name, Server_DSN as the Server DSN. And execute the command:
ttIsqlCS -connStr "DSN=Client_DSN"
Alternatively, define the logical server name logical_server with server.mycompany.com as the Network Address and the default port number as the Network Port. Define a Client DSN with logical_server as the Server name, Server_DSN as the Server DSN. Overwrite the port number in the command:
ttIsqlCS -connStr "DSN=Client_DSN; TCP_Port=53385"
Alternatively, define the Server in the connection string. In this case you do not need to define a Client DSN, nor a logical server name.
ttIsqlCS -connStr "TTC_Server=server.mycompany.com; TTC_Server_DSN=Server_DSN; TCP_Port=53385"
To test client application connections to TimesTen data stores:
On the Windows Desktop, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel.
Double click ODBC. This opens the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Select the TimesTen Client DSN whose connection you want to test and click Configure. This opens the TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog.

Click Test TimesTen Server Connection to test the connection to TimesTen Server.
The ODBC Data Source Administrator attempts to connect to TimesTen Server Daemon and displays messages to indicate if it was successful. During this test TimesTen Client verifies that:
ODBC, Windows sockets and TimesTen Client are installed on the client machine.
The server specified in the Server Name or Network Address field of the TimesTen Client DSN Setup dialog is defined and the corresponding machine exists.
The TimesTen Server Daemon is running on the server machine.
Click Test Data Source Connection to test the connection to the Server DSN. The ODBC Data Source Administrator attempts to connect to the TimesTen Server DSN and displays messages to indicate whether it was successful.
During this test, TimesTen Client verifies that:
The Server DSN specified in the Server DSN field is defined on the server machine.
A client application can connect to the Server DSN.
On UNIX, you define logical server names by editing the TTCONNECT.INI file and you define Client DSNs by editing the user ODBC.INI file for user DSN or the system ODBC.INI file for system DSNs. For a description of user and system DSNs, see "Data source names".
This section includes the following topics:
When TimesTen looks for a specific DSN, it looks in the following locations in this order:
The file referenced by the ODBCINI environment variable, if it is set.
The .odbc.ini file in the user's home directory, if the ODBCINI environment variable is not set.
The file referenced by the SYSODBCINI environment variable, if it is set
The sys.odbc.ini file in the daemon home directory, if the SYSODBCINI environment variable is not set.
Define logical server names in a file named by the SYSTTCONNECTINI environment variable. This file is referred to as the TTCONNECT.INI file. The file contains a description, a network address and a port number.
The Network Address must be one of:
| Type of connection | Network address |
|---|---|
| Local client/server connection that uses UNIX domain sockets | ttLocalHost |
| Local client/server connection that uses shared memory for inter-process communication | ttShmHost |
| Remote client/server connection | The name of the machine where the TimesTen Server is running. For example, server. mycompany.com |
TimesTen searches for the logical server in this order:
In the file specified by the SYSTTCONNECTINI environment variable, if it is set
In the daemon_home_dir/sys.ttconnect.ini file
Example 2-1 Defining a logical server name
This example from a TTCONNECT.INI file defines a logical server name, ttserver_logical, for a TimesTen Server daemon running on the machine server.mycompany.com and listening on port 53385. The instance name of the TimesTen installation is tt1121.
[ttserver_logical] Description=TimesTen Server 11.2.1 Network_Address=server.mycompany.com TCP_Port=53385
Example 2-2 Using UNIX domain sockets for communication
If both the client and server are on the same UNIX machine, applications using the TimesTen Client ODBC driver may improve performance by using UNIX domain sockets for communication.
The logical server name must also define the port number on which the TimesTen Server Daemon is listening so that multiple instances of the same version of TimesTen Server Daemon can be run on the same machine. To achieve this, the logical server name definition in TTCONNECT.INI file might look like:
[LocalHost_tt1121_32] Description= Local TimesTen Server TimesTen release 11.2.1 through domain sockets Network_Address=ttLocalHost TCP_PORT=53385
Example 2-3 Configuring shared memory for inter-process communication
If both the client and server are on the same machine, applications can use shared memory for inter-process communication. This may result in the best performance.
The logical server name must also define the port number on which the TimesTen Server Daemon is listening in order to make the initial connection. To achieve this, the logical server name definition in TTCONNECT.INI file might look like:
[ShmHost_tt1121] Description= Local TimesTen Server TimesTen release 11.2.1 through shared memory Network_Address=ttShmHost TCP_PORT=53385
In the ODBC Data Sources section of the ODBC.INI file, add an entry for the Client DSN. Each entry in this section lists the data source and the name of the ODBC driver that the data source uses. Use the following format for data source entries.
[ODBC Data Sources] data-source-name=name-of-ODBC-driver
For example, to add the RunDataCS_tt1121_32 data source and associate it with the TimesTen Client ODBC driver, make the following entry in the ODBC Data Sources section of the ODBC.INI file.
[ODBC Data Sources] RunDataCS_tt1121_32=TimesTen Client 11.2.1
After the ODBC Data Sources section, add an entry to specify the connection attributes for each data source you have defined. Each data source listed in the ODBC Data Sources section of the ODBC.INI file requires a data source specification section.
The following is an example specification of the TimesTen Client example DSN RunData_tt1121_32.
[RunDataCS_tt1121_32] TTC_Server=ttserver_logical TTC_Server_DSN=RunData_tt1121_32
For a description of the Client DSN attributes used in the ODBC.INI file, see "Data Store Attributes" in the Oracle TimesTen In-Memory Database Reference.
You can configure automatic client failover for data stores that have active standby pair replication schemes. This enables the client to fail over automatically to the server on which the standby data store resides.
In the ODBC.INI file, set TTC_SERVER2 to the server on which the standby data store resides. Set TTC_SERVER_DSN2 to the name of the standby data store.
For example:
[MYDSN FAILOVER] TTC_SERVER=localhost TTC_SERVER_DSN=MYDSN TTC_Timeout=60000 ConnectionCharacterSet=AL32UTF8 TTC_SERVER2=localhost TTC_SERVER_DSN2=MYDSNSTANDBY
In this example, the TimesTen Client application machine is a 32-bit Solaris machine, client.mycompany.com. The client application is accessing the Server DSN RunData_tt1121_32 on the remote server machine, another 32-bit Solaris machine, server.mycompany.com. The logical name of the server is ttserver_logical. The instance name of the TimesTen installation is tt1121_32.
On the server machine server.mycompany.com, use the ttStatus utility to verify that the TimesTen Server is running and to verify the port number on which it is listening.
Verify that the Server DSN RunData_tt1121_32 exists in the system ODBC.INI file on server.mycompany.com.
There should be an entry in the ODBC.INI file as follows:
[RunData_tt1121_32]
Driver=install_dir/lib/libtten.so
DataStore=install_dir/server/RunData_tt1121_32
Create a logical Server Name entry for the remote TimesTen Server in the TTCONNECT.INI file on client.mycompany.com.
[ttserver_logical] # This value for TCP_Port should correspond to the # value reported by ttStatus when verifying that the # server is running Network_Address=server.mycompany.com TCP_Port=53385
See "Creating and configuring Client DSNs on UNIX" for information on the creating a TTCONNECT.INI file.
On the client machine, client.mycompany.com, create a Client DSN corresponding to the remote Server DSN, RunData_tt1121_32.
There should be an entry in the ODBC.INI file as follows:
[RunDataCS_tt1121_32] TTC_SERVER=ttserver_logical TTC_SERVER_DSN=RunData_tt1121_32
See "User and system DSNs" for information on the location of the proper ODBC.INI file.
Run the client application from the machine client.mycompany.com using the Client DSN, RunDataCS_tt1121_32. The example below uses the ttIsql program that is installed with TimesTen Client.
ttIsqlCS -connStr "DSN=RunDataCS_tt1121_32"
The next example describes how to access a TimesTen Server that is listening on a port numbered other than the default port number.
Let us consider the Network Address of the TimesTen Server is server.mycompany.com and the Server is listening on Port 53385. The following methods can be used to connect to a Server DS:
Define the logical server name logical_server with server.mycompany.com as the Network Address and 53385 as the Network Port. Define a Client DSN with logical_server as the server name, Server_DSN as the Server DSN. Execute the command:
ttIsqlCS -connStr "DSN=Client_DSN"
Alternatively, define the logical server name logical_server with server.mycompany.com as the Network Address and the default port number as the Network Port. Define a Client DSN with logical_server as the server name, Server_DSN as the Server DSN. Overwrite the port number in the command:
ttIsqlCS -connStr "DSN=Client_DSN; TCP_Port=53385"
Alternatively, define the server in the connection string. In this case you do not need to define a Client DSN, nor a logical server name.
ttIsqlCS -connStr "TTC_Server=server.mycompany.com; TTC_Server_DSN=Server_DSN; TCP_Port=53385"
To test client application connections to TimesTen data stores:
Verify that the client machine can access the server machine.
Run ping from the client machine to see if a response is received from the server machine.
Verify that the TimesTen Server Daemon is running on the server machine.
Use telnet to connect to the port on which the TimesTen Server Daemon is listening. For example:
telnet server.mycompany.com 53385
If you successfully connect to the TimesTen Server Daemon, you will see a message similar to:
Connected to server.mycompany.com
If the server machine responds to a command, but TimesTen Server Daemon does not, the TimesTen Server Daemon may not be running. In the case of a failed connection, you will see a message similar to:
telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: Connection refused
Use the ttStatus utility on the server machine to determine the status and port number of the TimesTen Server. Generally, the TimesTen Server Daemon is started at installation time. If the TimesTen Server Daemon is not running, you must start it. For information on starting the TimesTen Server, see "Modifying the TimesTen Server daemon options".
Verify that the client application can connect to the data store. If you cannot establish a connection to the data store, check that the TTCONNECT.INI file contains the correct information.
If the information in the TTCONNECT.INI file is correct, check that a Server DSN corresponding to the data store has been defined properly in the system ODBC.INI file on the machine where the data store resides and where the TimesTen Server Daemon is running.
TimesTen uses theTTCONNECT.INI file to define the names and attributes for servers and the mappings between logical server names and their network addresses. This information is stored on machine where the TimesTen Client is installed. By default, the TTCONNECT.INI file is install_dir/sys.ttconnect.ini.
To override the name and location of this file at runtime, set the SYSTTCONNECTINI environment variable to the name and location of the TTCONNECT.INI file before launching the TimesTen application.
You can define short-hand names for TimesTen Servers on UNIX in the TTCONNECT.INI file. The format of a TimesTen Server specification in the TTCONNECT.INI file is shown in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 TimesTen Server format in the TTCONNECT.INI file
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
[ |
Short name of the TimesTen you wish to define |
|
|
Description of the TimesTen Server |
|
|
The DNS name, host name or IP address of the machine on which the TimesTen Server is running. |
|
|
The TCP/IP port number where the TImesTen Server is running. Default for TimesTen release 11.2.1 is 53385 for 32-bit platforms and 53389 for 64-bit platforms. |
For example, the server specification for a remote TimesTen Server might appear as:
[ttserver] Description=TimesTen Client/Server Network_Address=server.company.com TCP_Port=53385
For a local TimesTen Client/Server application that is using UNIX domain sockets, the network address must be defined as ttLocalHost. The server specification might appear as:
[LocalHost1121] Description=Shm TimesTen Client/Server Network_Address=ttLocalHost TCP_Port=53385
For a TimesTen Client/Server application that is using a shared memory segment for inter-process communication, the network address must be defined as ttShmHost. The server specification might appear as:
[ShmHost1121] Description=Shm TimesTen Client/Server Network_Address=ttShmHost TCP_Port=53385