| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database PL/SQL Language Reference 11g Release 2 (11.2) Part Number E10472-05 |
|
|
View PDF |
The OPEN FOR statement associates a cursor variable with a multiple-row query, allocates database resources to process the query, identifies the result set, and positions the cursor before the first row of the result set. (If the query has a FOR UPDATE clause, processing the query includes locking the rows of the result set—see "SELECT FOR UPDATE and FOR UPDATE Cursors".)
Topics:
Syntax
open_for_statement ::=
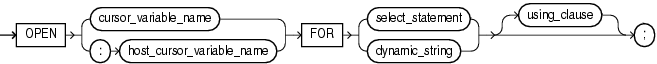
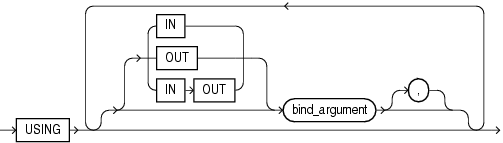
using_clause ::=
Semantics
open_for_statement
cursor_variable_name
The name of a cursor variable. If the cursor variable is the formal parameter of a subprogram, it must not have a return type. For information about cursor variables as subprogram parameters, see "Cursor Variables as Subprogram Parameters".
host_cursor_variable_name
The name of a cursor variable that was declared in a PL/SQL host environment and passed to PL/SQL as a bind argument. The data type of the cursor variable is compatible with the return type of any PL/SQL cursor variable. Do not put space between the colon (:) and host_cursor_variable_name.
select_statement
A string literal, string variable, or string expression; of type CHAR, VARCHAR2, or CLOB; that represents a multiple-row SQL SELECT statement (not a PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement).
dynamic_string
A string literal, string variable, or string expression; of type CHAR, VARCHAR2, or CLOB; that represents a multiple-row SQL SELECT statement (not a PL/SQL SELECT INTO statement).
using_clause
Specifies bind arguments.
Restrictions on using_clause
Use if and only if select_statement or dynamic_sql_stmt includes placeholders for bind arguments.
If dynamic_sql_stmt has a RETURNING INTO clause, using_clause can contain only IN bind arguments. The bind arguments in the RETURNING INTO clause are OUT bind arguments by definition.
bind_argument
An expression whose value replaces its corresponding placeholder in select_statement or dynamic_string at run time. You must specify a bind_argument for every placeholder.
IN, OUT, IN OUT
Parameter modes of bind arguments. An IN bind argument passes its value to the select_statement or dynamic_string. An OUT bind argument stores a value that dynamic_string returns. An IN OUT bind argument passes its initial value to dynamic_string and stores a value that dynamic_string returns. The default parameter mode for bind_argument is IN.
Examples
Example 6-31, "Stored Procedure to Open Cursor Variables with Different Queries"
Example 7-4, "Native Dynamic SQL with OPEN FOR, FETCH, and CLOSE Statements"
Related Topics
In this chapter:
In other chapters: